- 1 Introduction
- 2 Import the Libraries and the Data
- 3 Definition of required Functions
- 4 Text Pre-Processing
- 5 Final Words
- 6 Conclusion
1 Introduction
Let’s move on to the final part of the post series on Pre-Processing Steps in NLP: Word Removal
For this publication the processed dataset Amazon Unlocked Mobile from the statistic platform “Kaggle” was used. Furthermore I will use the last state of the example string and the saved frequency tables I created in my last post. You can download all files from my “GitHub Repository”.
2 Import the Libraries and the Data
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import pickle as pk
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import unicodedata
import re
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.corpus import wordnet
from nltk import pos_tag
from nltk import ne_chunk
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
from nltk.stem.wordnet import WordNetLemmatizer
from nltk.probability import FreqDist
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from wordcloud import WordCloudpd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', 30)df = pd.read_csv('Amazon_Unlocked_Mobile_small_Part_V.csv')
df.head(3).T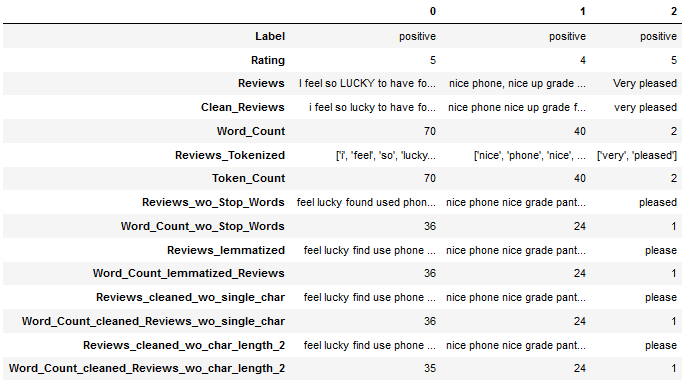
df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char'] = df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char'].astype(str)clean_text_wo_single_char = pk.load(open("clean_text_wo_single_char.pkl",'rb'))
clean_text_wo_single_char
In addition to the DataFrame and the Example String, we load the previously saved frequency tables from the post NLP - Text Pre-Processing V (Text Exploration) at this point.
df_most_common_words = pd.read_csv('df_most_common_words.csv')
df_least_common_words = pd.read_csv('df_least_common_words.csv')
df_most_common_words_text_corpus = pd.read_csv('df_most_common_words_text_corpus.csv')
df_least_common_words_text_corpus = pd.read_csv('df_least_common_words_text_corpus.csv')3 Definition of required Functions
All functions are summarized here. I will show them again where they are used during this post if they are new and have not been explained yet.
def word_count_func(text):
'''
Counts words within a string
Args:
text (str): String to which the function is to be applied, string
Returns:
Number of words within a string, integer
'''
return len(text.split())def single_word_remove_func(text, word_2_remove):
'''
Removes a specific word from string, if present
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Removes the defined word from the created tokens
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
word_2_remove (str): Word to be removed from the text, string
Returns:
String with removed words
'''
word_to_remove = word_2_remove
words = word_tokenize(text)
text = ' '.join([word for word in words if word != word_to_remove])
return textdef multiple_word_remove_func(text, words_2_remove_list):
'''
Removes certain words from string, if present
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Removes the defined words from the created tokens
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
words_2_remove_list (list): Words to be removed from the text, list of strings
Returns:
String with removed words
'''
words_to_remove_list = words_2_remove_list
words = word_tokenize(text)
text = ' '.join([word for word in words if word not in words_to_remove_list])
return textdef most_freq_word_func(text, n_words=5):
'''
Returns the most frequently used words from a text
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Uses the FreqDist function to determine the word frequency
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
Returns:
List of the most frequently occurring words (by default = 5)
'''
words = word_tokenize(text)
fdist = FreqDist(words)
df_fdist = pd.DataFrame({'Word': fdist.keys(),
'Frequency': fdist.values()})
df_fdist = df_fdist.sort_values(by='Frequency', ascending=False)
n_words = n_words
most_freq_words_list = list(df_fdist['Word'][0:n_words])
return most_freq_words_listdef most_rare_word_func(text, n_words=5):
'''
Returns the most rarely used words from a text
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Uses the FreqDist function to determine the word frequency
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
Returns:
List of the most rarely occurring words (by default = 5)
'''
words = word_tokenize(text)
fdist = FreqDist(words)
df_fdist = pd.DataFrame({'Word': fdist.keys(),
'Frequency': fdist.values()})
df_fdist = df_fdist.sort_values(by='Frequency', ascending=False)
n_words = n_words
most_rare_words_list = list(df_fdist['Word'][-n_words:])
return most_rare_words_list4 Text Pre-Processing
4.1 (Text Cleaning)
I have already described this part in an earlier post. See here: Text Cleaning
4.2 (Tokenization)
I have already described this part in an earlier post. See here: Text Pre-Processing II-Tokenization
4.3 (Stop Words)
I have already described this part in an earlier post. See here: Text Pre-Processing II-Stop Words
4.4 (Digression: POS & NER)
I have already described this part in an earlier post. See here: Text Pre-Processing III-POS & NER
4.5 (Normalization)
I have already described this part in an earlier post. See here: Text Pre-Processing III-Normalization
4.6 (Removing Single Characters)
I have already described this part in an earlier post. See here: Text Pre-Processing IV-Removing Single Characters
4.7 (Text Exploration)
I have already described this part in the previous post. See here: Text Pre-Processing V-Text Exploration
4.8 Removing specific Words
Sometimes it is helpful or even necessary to specifically remove certain words.
In this and the two following chapters, I will refer to the frequency tables from the Text Exploration chapter and will always recall them so that it is clear to the reader to which processing stage of each text I am referring. All operations from this and the following two chapters will be performed on the example string ‘clean_text_wo_single_char’ and the column ‘Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char’. Furthermore, at the end of this post, I will again give an overview of which operations I applied to which source column and what happened in the process, so that there is no confusion for the reader.
But now let’s take a look at this tongue twister as an example:
text_for_word_removal = \
"Give papa a cup of proper coffe in a copper coffe cup."
text_for_word_removal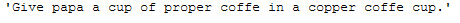
4.8.1 Single Word Removal
The removal of individual words can be done with the help of this function:
def single_word_remove_func(text, word_2_remove):
'''
Removes a specific word from string, if present
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Removes the defined word from the created tokens
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
word_2_remove (str): Word to be removed from the text, string
Returns:
String with removed words
'''
word_to_remove = word_2_remove
words = word_tokenize(text)
text = ' '.join([word for word in words if word != word_to_remove])
return textsingle_word_remove_func(text_for_word_removal, "coffe")
4.8.2 Multiple Word Removal
But often you have the problem of having to remove several words. To use the function shown above each time would be tedious. Therefore, here is a function that can remove multiple words from a sentence:
def multiple_word_remove_func(text, words_2_remove_list):
'''
Removes certain words from string, if present
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Removes the defined words from the created tokens
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
words_2_remove_list (list): Words to be removed from the text, list of strings
Returns:
String with removed words
'''
words_to_remove_list = words_2_remove_list
words = word_tokenize(text)
text = ' '.join([word for word in words if word not in words_to_remove_list])
return textThe application of this function can be done in several ways. Below are three examples of how to do this:
multiple_word_remove_func(text_for_word_removal, ["coffe", "cup"])
list_with_words = ["coffe", "cup"]
multiple_word_remove_func(text_for_word_removal, list_with_words)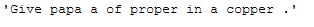
params= [text_for_word_removal,
["coffe", "cup"]]
multiple_word_remove_func(*params)
4.8.3 Application to the Example String
For this, let’s look at our last state with the String example:
clean_text_wo_single_char
For this purpose, we also take a look at the frequency distribution of the words:
plt.figure(figsize=(11,7))
plt.bar(df_most_common_words['Word'],
df_most_common_words['Frequency'])
plt.xticks(rotation = 45)
plt.xlabel('Most common Words')
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.title("Frequency distribution of the 25 most common words")
plt.show()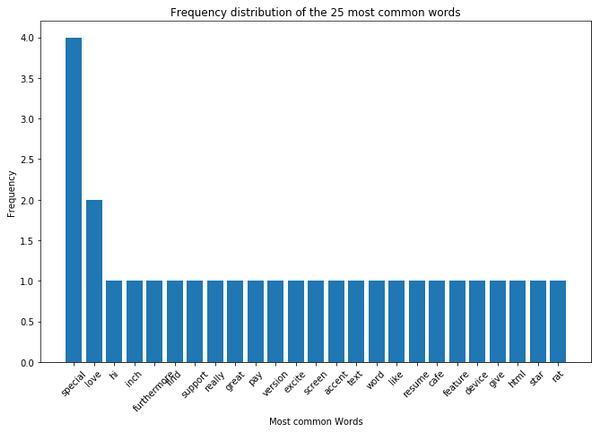
df_most_common_words.head()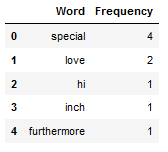
plt.figure(figsize=(11,7))
plt.bar(df_least_common_words['Word'],
df_least_common_words['Frequency'])
plt.xticks(rotation = 45)
plt.xlabel('Least common Words')
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.title("Frequency distribution of the 10 least common words")
plt.show()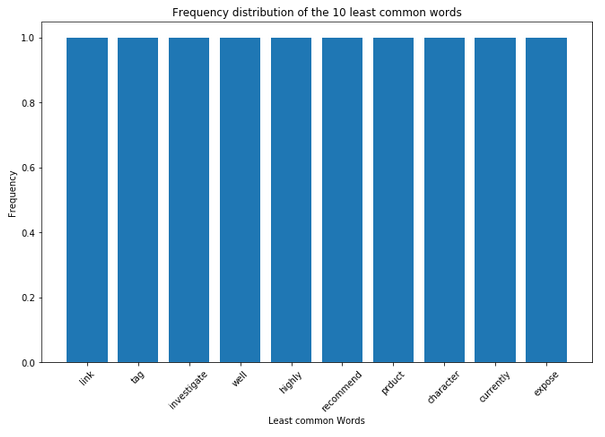
df_least_common_words.tail()
4.8.3.1 with Single Word Removal
In the following I would like to remove the word ‘special’, because it appears too often in the example string.
clean_text_wo_specific_word = single_word_remove_func(clean_text_wo_single_char, "special")
clean_text_wo_specific_word
print('Number of words (bevore single word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(clean_text_wo_single_char)))
print('Number of words (after single word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(clean_text_wo_specific_word)))
Worked wonderfully. Since the word ‘special’ appears 4 times, this difference can also be seen in the print statement shown above.
4.8.3.2 with Multiple Word Removal
Now, in addition, I would like to remove more words, which I think are not profitable.
clean_text_wo_specific_words = multiple_word_remove_func(clean_text_wo_specific_word,
["expose", "currently", "character"])
clean_text_wo_specific_words
print('Number of words (bevore multiple word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(clean_text_wo_specific_word)))
print('Number of words (after multiple word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(clean_text_wo_specific_words)))
This operation also worked the way we wanted it to. The three words we removed each appeared only once in the text. Hence the difference of 3.
4.8.4 Application to the DataFrame
Here again we take a look at the frequency distribution of the words from the column ‘Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char’. This is the column I decided to work on in the Removing Single Characters’ chapter.
plt.figure(figsize=(11,7))
plt.bar(df_most_common_words_text_corpus['Word'],
df_most_common_words_text_corpus['Frequency'])
plt.xticks(rotation = 45)
plt.xlabel('Most common Words')
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.title("Frequency distribution of the 25 most common words")
plt.show()
df_most_common_words_text_corpus.head()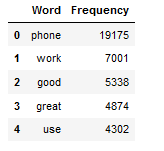
In the last chapter Text Exploration I split this column again according to the evaluation type (‘positive’, ‘neutral’ and ‘negative’) and made separate visualizations of the word frequency for each. The result was that the word ‘phone’ occurs disproportionately often in all three sub-sets compared to the other words. I can therefore assume that this word is not particularly profitable for a later classification and would therefore like to remove it.
plt.figure(figsize=(11,7))
plt.bar(df_least_common_words_text_corpus['Word'],
df_least_common_words_text_corpus['Frequency'])
plt.xticks(rotation = 45)
plt.xlabel('Least common Words')
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.title("Frequency distribution of the 10 least common words")
plt.show()
df_least_common_words_text_corpus.tail()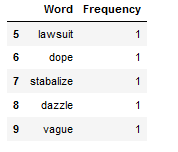
4.8.4.1 with Single Word Removal
In the following, I will now remove the word ‘phone’ from all rows in the ‘Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char’ column.
df["Reviews_cleaned_wo_specific_word"] = df.apply(lambda x: single_word_remove_func(x["Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char"],
"phone"), axis = 1)Calculating the number of words per line and saving it in a separate column as I have done in the past chapters is in my opinion not useful at this point.
To check that the word ‘phone’ has been deleted from all lines, it is useful to create a new text corpus and compare the number of words. I had already created the first text corpus in the last chapter, but for the sake of completeness I will do it again here.
text_corpus_original = df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char'].str.cat(sep=' ')
text_corpus_wo_specific_word = df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_specific_word'].str.cat(sep=' ')
print('Number of words (bevore single word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_original)))
print('Number of words (after single word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_specific_word)))
print()
print('Diff: ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_original) - word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_specific_word)))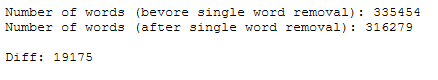
The operation also worked well on the data set. If you compare the calculated difference with the word frequency table above (df_most_common_words_text_corpus), you can see that the word ‘phone’ has been completely removed from all lines.
4.8.4.2 with Multiple Word Removal
Also at this point I will now remove other words from the newly generated ‘Reviews_cleaned_wo_specific_word’ column that I feel are not profitable. To do this I will take the 3 words that are at the very end of the frequency table (df_least_common_words_text_corpus).
df["Reviews_cleaned_wo_specific_words"] = df.apply(lambda x: multiple_word_remove_func(x["Reviews_cleaned_wo_specific_word"],
["stabalize", "dazzle", "vague"]), axis = 1)Now we compare the text corpuses with each other again.
text_corpus_wo_specific_words = df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_specific_words'].str.cat(sep=' ')
print('Number of words (bevore multiple word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_specific_word)))
print('Number of words (after multiple word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_specific_words)))
print()
print('Diff: ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_specific_word) - word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_specific_words)))
This result also suggests a positive implementation of the operation. If we add the frequency values of the last three words in the frequency table (df_least_common_words_text_corpus) above, we get the sum of 3, which is congruent with the difference shown above.
4.9 Removing Frequent words
In the previously shown chapter, I showed how to remove certain words from a text corpus or from all rows in a column. However, it is often the case that you have far too many of them for me to want to name them individually in the single_word_remove function or the multiple_word_remove function.
For this reason I have written functions for this and the following chapter, which give me a list of common or rare words, which I can then remove from my text.
But be careful when removing such words. They can nevertheless (even if one would not suspect it at first) be profitable for the later algorithm. I therefore recommend to always save the new text modules in a separate column or object and to check later with the help of the validation of the algorithm whether the opearation was useful or not.
text_for_freq_word_removal = \
"Peter Pepper picked a pack of pickled peppers. How many pickled peppers did Peter Pepper pick?"
text_for_freq_word_removal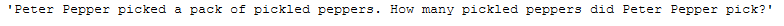
def most_freq_word_func(text, n_words=5):
'''
Returns the most frequently used words from a text
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Uses the FreqDist function to determine the word frequency
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
Returns:
List of the most frequently occurring words (by default = 5)
'''
words = word_tokenize(text)
fdist = FreqDist(words)
df_fdist = pd.DataFrame({'Word': fdist.keys(),
'Frequency': fdist.values()})
df_fdist = df_fdist.sort_values(by='Frequency', ascending=False)
n_words = n_words
most_freq_words_list = list(df_fdist['Word'][0:n_words])
return most_freq_words_listmost_freq_words_list = most_freq_word_func(text_for_freq_word_removal, n_words=2)
most_freq_words_list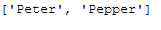
multiple_word_remove_func(text_for_freq_word_removal, most_freq_words_list)
4.9.1 Application to the Example String
(!) Important to note here: I use again the same state of the example string as at the beginning of the chapter Removing specific Words where I have not yet removed the specific words!
clean_text_wo_single_char
Here again the frequency distribution in visual and tabular version:
plt.figure(figsize=(11,7))
plt.bar(df_most_common_words['Word'],
df_most_common_words['Frequency'])
plt.xticks(rotation = 45)
plt.xlabel('Most common Words')
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.title("Frequency distribution of the 25 most common words")
plt.show()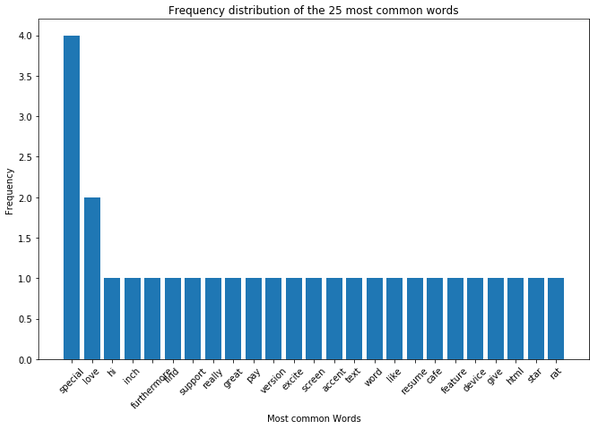
df_most_common_words.head()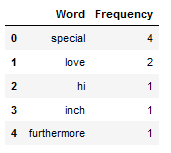
most_freq_words_list_Example_String = most_freq_word_func(clean_text_wo_single_char, n_words=2)
most_freq_words_list_Example_String
clean_text_wo_freq_words = multiple_word_remove_func(clean_text_wo_single_char,
most_freq_words_list_Example_String)
clean_text_wo_freq_words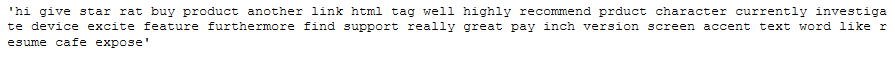
4.9.2 Application to the DataFrame
(!) Important to note here: I use the column ‘Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char’ as in the chapter Removing specific Words because at this point I don’t want specific words are already removed from the text.
plt.figure(figsize=(11,7))
plt.bar(df_most_common_words_text_corpus['Word'],
df_most_common_words_text_corpus['Frequency'])
plt.xticks(rotation = 45)
plt.xlabel('Most common Words')
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.title("Frequency distribution of the 25 most common words")
plt.show()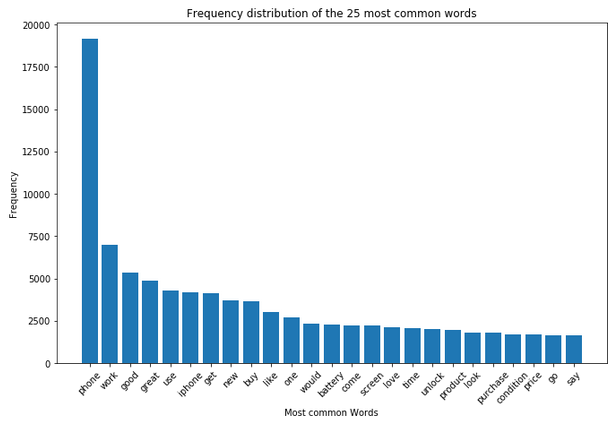
df_most_common_words_text_corpus.head(10)
most_freq_words_list_DataFrame = most_freq_word_func(text_corpus_original, n_words=2)
most_freq_words_list_DataFrame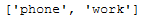
df["Reviews_cleaned_wo_freq_words"] = df.apply(lambda x: multiple_word_remove_func(x["Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char"],
most_freq_words_list_DataFrame), axis = 1)text_corpus_wo_freq_words = df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_freq_words'].str.cat(sep=' ')
print('Number of words (bevore freq word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_original)))
print('Number of words (after freq word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_freq_words)))
print()
print('Diff: ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_original) - word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_freq_words)))
4.10 Removing Rare words
We will probably use this function more often, which allows us to identify rarely occurring words in a text and then remove them.
text_for_rare_word_removal = \
"Sue sells seashells by the seashore. The seashells Sue sells are seashells Sue is sure."
text_for_rare_word_removal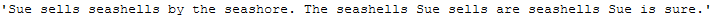
def most_rare_word_func(text, n_words=5):
'''
Returns the most rarely used words from a text
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Uses the FreqDist function to determine the word frequency
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
Returns:
List of the most rarely occurring words (by default = 5)
'''
words = word_tokenize(text)
fdist = FreqDist(words)
df_fdist = pd.DataFrame({'Word': fdist.keys(),
'Frequency': fdist.values()})
df_fdist = df_fdist.sort_values(by='Frequency', ascending=False)
n_words = n_words
most_rare_words_list = list(df_fdist['Word'][-n_words:])
return most_rare_words_listmost_rare_words_list = most_rare_word_func(text_for_rare_word_removal, n_words=3)
most_rare_words_list
multiple_word_remove_func(text_for_rare_word_removal, most_rare_words_list)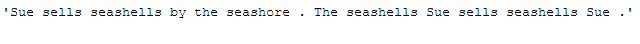
4.10.1 Application to the Example String
(!) Important to note here: I use again the same state of the example string as at the beginning of the chapter Removing specific Words where I have not yet removed the specific words!
clean_text_wo_single_char
plt.figure(figsize=(11,7))
plt.bar(df_least_common_words['Word'],
df_least_common_words['Frequency'])
plt.xticks(rotation = 45)
plt.xlabel('Least common Words')
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.title("Frequency distribution of the 10 least common words")
plt.show()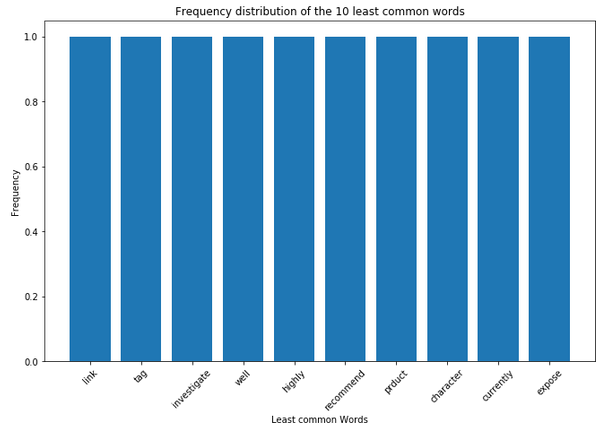
df_least_common_words.tail()
most_rare_words_list_Example_String = most_rare_word_func(clean_text_wo_single_char, n_words=4)
most_rare_words_list_Example_String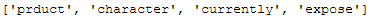
clean_text_wo_rare_words = multiple_word_remove_func(clean_text_wo_single_char,
most_rare_words_list_Example_String)
clean_text_wo_rare_words
4.10.2 Application to the DataFrame
(!) Important to note here: I use the column ‘Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char’ as in the chapter Removing specific Words because at this point I don’t want specific words are already removed from the text.
plt.figure(figsize=(11,7))
plt.bar(df_least_common_words_text_corpus['Word'],
df_least_common_words_text_corpus['Frequency'])
plt.xticks(rotation = 45)
plt.xlabel('Least common Words')
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.title("Frequency distribution of the 10 least common words")
plt.show()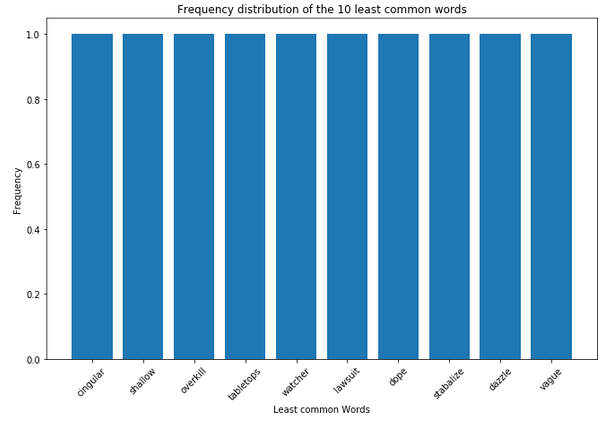
df_least_common_words_text_corpus
most_rare_words_list_DataFrame = most_rare_word_func(text_corpus_original, n_words=4)
most_rare_words_list_DataFrame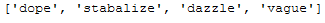
df["Reviews_cleaned_wo_rare_words"] = df.apply(lambda x: multiple_word_remove_func(x["Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char"],
most_rare_words_list_DataFrame), axis = 1)text_corpus_wo_rare_words = df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_rare_words'].str.cat(sep=' ')
print('Number of words (bevore rare word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_original)))
print('Number of words (after rare word removal): ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_rare_words)))
print()
print('Diff: ' + str(word_count_func(text_corpus_original) - word_count_func(text_corpus_wo_rare_words)))
5 Final Words
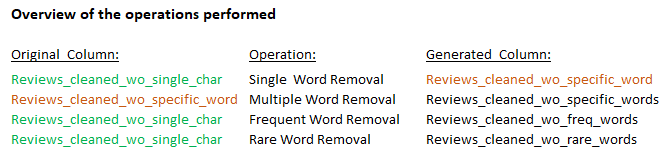
When removing certain words, I applied the operation to the previously created column. Otherwise, I always used our original column ‘Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char’ as the basis for the functions.
What I didn’t do in this post was generate a separate column where I removed both the frequented words and the rarely occurring words. My tip at this point would be to create different columns where you have removed different types and different number of words and then see which data base the algorithm performs best on.