- 1 Introduction
- 2 Import the libraries
- 3 Data pre-processing
- 4 Feature Extraction without Data Augmentation
- 4.1 Name Definitions
- 4.2 Parameter Settings
- 4.3 Instantiating the VGG19 convolutional base
- 4.4 Feature Extraction
- 4.6 Callbacks
- 4.7 Fitting the model
- 4.8 Obtaining the best model values
- 4.9 Obtaining class assignments
- 4.10 Validation
- 4.11 Load best model
- 4.12 Model Testing
- 4.13 Test Out of the Box Pictures
- 5 Feature Extraction with Data Augmentation
- 5.1 Name Definitions
- 5.2 Parameter Settings
- 5.3 Instantiating the VGG19 convolutional base
- 5.4 Instantiating a densely connected classifier
- 5.5 Callbacks
- 5.6 Fitting the model
- 5.7 Obtaining the best model values
- 5.8 Obtaining class assignments
- 5.9 Validation
- 5.10 Load best model
- 5.11 Model Testing
- 5.12 Test Out of the Box Pictures
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 Link to the GitHub Repository
1 Introduction
In my post Computer Vision - Convolutional Neural Network I showed how to train a Convolutional Neural Network for binary image classification. Now I will try to improve this model again using Transfer Learning.
Keras offers several applications that can be used for transfer learning. I used the VGG19 to train my binary image classifier below.
For this publication I used the images from the cats and dogs dataset from the statistics platform “Kaggle”. You can download the used data from my “GitHub Repository”.
2 Import the libraries
from preprocessing_CNN import Train_Validation_Test_Split
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
import shutil
import pickle as pk
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from keras import layers
from keras import models
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.models import load_model
from keras.applications import VGG193 Data pre-processing
How the data for a CNN model training must be prepared I have already explained in this post: Computer Vision - Convolutional Neural Network
The exact functionality of the code I have explained in this post: Automate the Boring Stuff
Please download the two folders cats and dogs from my “GitHub Repository” and navigate to the project’s root directory in the terminal. The notebook must be started from the location where the two files are stored.
3.1 Train-Validation-Test Split
For this please download the preprocessing_CNN.py file from my “GitHub Repository” and place this file next to the folders cats and dogs and start your Jupyter notebook from here.
c_train, d_train, c_val, d_val, c_test, d_test = Train_Validation_Test_Split('cats', 'dogs')
3.2 Obtaining the lists of randomly selected images
list_cats_training = c_train
list_dogs_training = d_train
list_cats_validation = c_val
list_dogs_validation = d_val
list_cats_test = c_test
list_dogs_test = d_test3.3 Determination of the directories
root_directory = os.getcwd()
train_dir = os.path.join(root_directory, 'cats_and_dogs\\train')
validation_dir = os.path.join(root_directory, 'cats_and_dogs\\validation')
test_dir = os.path.join(root_directory, 'cats_and_dogs\\test')3.4 Obtain the total number of training, validation and test images
num_cats_img_train = len(list_cats_training)
num_dogs_img_train = len(list_dogs_training)
num_train_images_total = num_cats_img_train + num_dogs_img_train
print('Total training cat images: ' + str(num_cats_img_train))
print('Total training dog images: ' + str(num_dogs_img_train))
print()
print('Total training images: ' + str(num_train_images_total))
num_cats_img_validation = len(list_cats_validation)
num_dogs_img_validation = len(list_dogs_validation)
num_validation_images_total = num_cats_img_validation + num_dogs_img_validation
print('Total validation cat images: ' + str(num_cats_img_validation))
print('Total validation dog images: ' + str(num_dogs_img_validation))
print()
print('Total validation images: ' + str(num_validation_images_total))
num_cats_img_test = len(list_cats_test)
num_dogs_img_test = len(list_dogs_test)
num_test_images_total = num_cats_img_test + num_dogs_img_test
print('Total test cat images: ' + str(num_cats_img_test))
print('Total test dog images: ' + str(num_dogs_img_test))
print()
print('Total test images: ' + str(num_test_images_total))
4 Feature Extraction without Data Augmentation
In this method, we run the convolutional basis over our dataset and record its output in a numpy array on disk. Subsequently, this data is then used as input to a standalone densely connected classifier.
4.1 Name Definitions
checkpoint_no = 'ckpt_1_CNN_with_TF_VGG19'
model_name = 'Cats_Dogs_CNN_TF_VGG19_epoch_30'4.2 Parameter Settings
img_height = 150
img_width = 150
input_shape = (img_height, img_width, 3)
n_batch_size = 32
n_epochs = 30
print('Input Shape: '+'('+str(img_height)+', '+str(img_width)+', ' + str(3)+')')
print('Batch Size: ' + str(n_batch_size))
print()
print('Number of Epochs: ' + str(n_epochs))
4.3 Instantiating the VGG19 convolutional base
We set include_top=False to get only the used conv-blocks and not the used dense layers.
VGG19_base = VGG19(weights='imagenet',
include_top=False,
input_shape=input_shape)
conv_base = VGG19_baseconv_base.summary()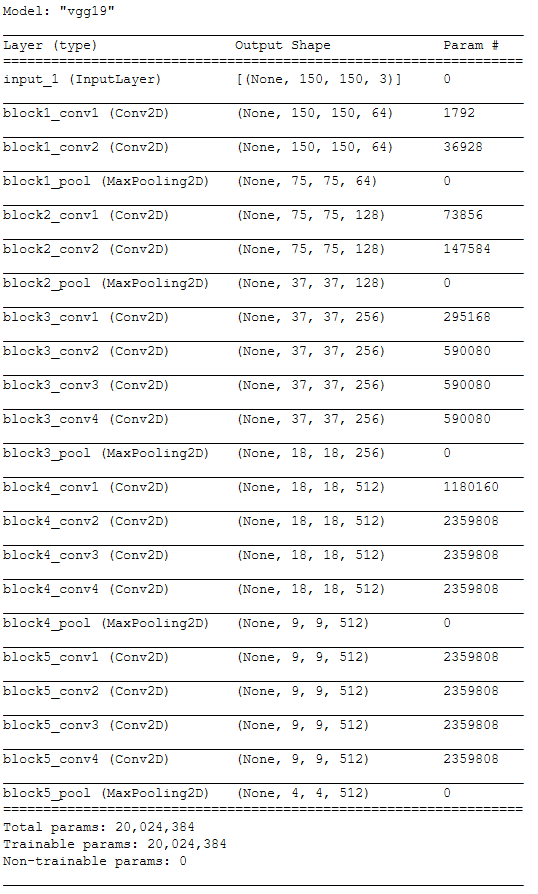
4.4 Feature Extraction
4.4.1 Get Output Shape of last Layer
df_temp = pd.DataFrame()
for layer in conv_base.layers:
layer_output_shape = layer.output_shape
df1 = {'Output_Shape': layer_output_shape}
df_temp = df_temp.append(df1, ignore_index=True)
df_temp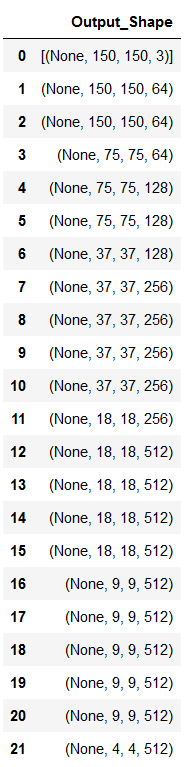
df_temp = df_temp.loc[df_temp.index == df_temp.index.max()]
df_temp = df_temp['Output_Shape'].iloc[0]
df_temp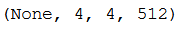
df_temp2 = pd.DataFrame(df_temp).T
df_temp2.columns= ['batch_size', 'pooled_rows', 'pooled_cols', 'channels']
df_temp2['pooled_rows'] = df_temp2['pooled_rows'].astype('int64')
df_temp2['pooled_cols'] = df_temp2['pooled_cols'].astype('int64')
df_temp2['channels'] = df_temp2['channels'].astype('int64')
df_temp2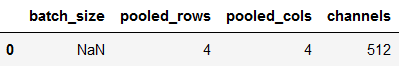
n_pooled_rows = df_temp2['pooled_rows'].iloc[0]
n_pooled_cols = df_temp2['pooled_cols'].iloc[0]
n_channels = df_temp2['channels'].iloc[0]
print('Number of pooled rows: ' + str(n_pooled_rows))
print('Number of pooled cols: ' + str(n_pooled_cols))
print('Number of channels: ' + str(n_channels))
4.4.2 Extracting features using the pretrained convolutional base
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
def extract_features(directory, sample_count):
features = np.zeros(shape=(sample_count, n_pooled_rows, n_pooled_cols, n_channels))
labels = np.zeros(shape=(sample_count))
generator = datagen.flow_from_directory(
directory,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=n_batch_size,
class_mode='binary')
class_assignments = generator.class_indices
i = 0
for inputs_batch, labels_batch in generator:
features_batch = conv_base.predict(inputs_batch)
features[i * n_batch_size : (i + 1) * n_batch_size] = features_batch
labels[i * n_batch_size : (i + 1) * n_batch_size] = labels_batch
i += 1
if i * n_batch_size >= sample_count:
break
return features, labels, class_assignmentstrain_features, train_labels, train_class_assignments = extract_features(train_dir, num_train_images_total)
validation_features, validation_labels, validation_class_assignments = extract_features(validation_dir, num_validation_images_total)
test_features, test_labels, test_class_assignments = extract_features(test_dir, num_test_images_total)
4.4.3 Reshape train-, validation- and test features
The extracted features are currently of shape (samples, 4, 4, 512). We are going to feed them to a densely connected classifier, so first we must flatten them to (samples, 8192).
train_features = np.reshape(train_features, (num_train_images_total,
n_pooled_rows * n_pooled_cols * n_channels))
validation_features = np.reshape(validation_features, (num_validation_images_total,
n_pooled_rows * n_pooled_cols * n_channels))
test_features = np.reshape(test_features, (num_test_images_total,
n_pooled_rows * n_pooled_cols * n_channels))4.5 Instantiating a densely connected classifier
4.5.1 Layer Structure
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Dense(256, activation='relu',
input_dim= n_pooled_rows * n_pooled_cols * n_channels))
model.add(layers.Dropout(0.5))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))model.summary()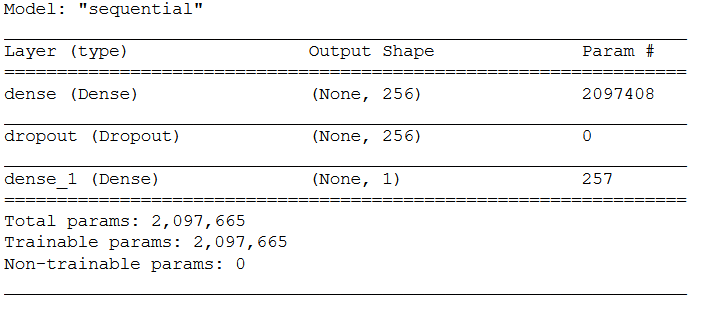
4.5.2 Configuring the model for training
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])4.6 Callbacks
# Prepare a directory to store all the checkpoints.
checkpoint_dir = checkpoint_no
if not os.path.exists(checkpoint_dir):
os.makedirs(checkpoint_dir)keras_callbacks = [ModelCheckpoint(filepath = checkpoint_dir + '/' + model_name,
monitor='val_loss', save_best_only=True, mode='auto')]4.7 Fitting the model
history = model.fit(
train_features, train_labels,
epochs = n_epochs,
batch_size = n_batch_size,
validation_data = (validation_features, validation_labels),
callbacks=keras_callbacks)
4.8 Obtaining the best model values
hist_df = pd.DataFrame(history.history)
hist_df['epoch'] = hist_df.index + 1
cols = list(hist_df.columns)
cols = [cols[-1]] + cols[:-1]
hist_df = hist_df[cols]
hist_df.to_csv(checkpoint_no + '/' + 'history_df_' + model_name + '.csv')
hist_df.head()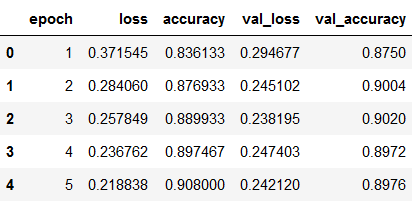
values_of_best_model = hist_df[hist_df.val_loss == hist_df.val_loss.min()]
values_of_best_model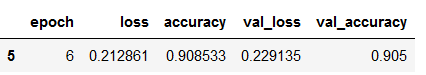
4.9 Obtaining class assignments
class_assignment = train_class_assignments
df = pd.DataFrame([class_assignment], columns=class_assignment.keys())
df_stacked = df.stack()
df_temp = pd.DataFrame(df_stacked).reset_index().drop(['level_0'], axis=1)
df_temp.columns = ['Category', 'Allocated Number']
df_temp.to_csv(checkpoint_no + '/' + 'class_assignment_df_' + model_name + '.csv')
print('Class assignment:', str(class_assignment))
4.10 Validation
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()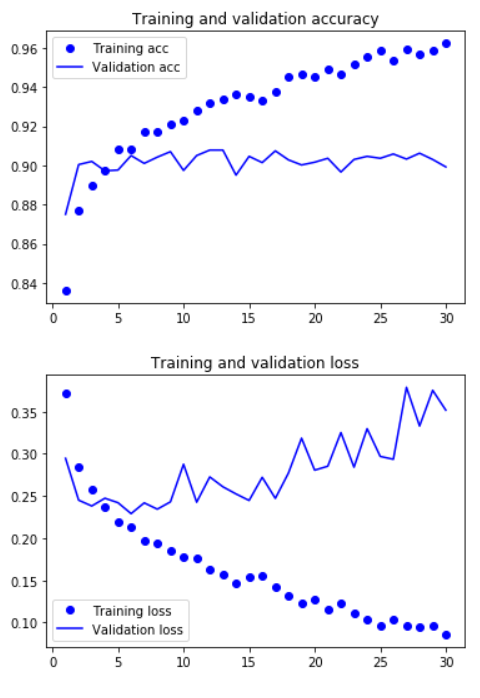
It looks like we have the problem of overfitting here. Let’s see what the subsequent tests bring for results.
4.11 Load best model
# Loading the automatically saved model
model_reloaded = load_model(checkpoint_no + '/' + model_name)
# Saving the best model in the correct path and format
root_directory = os.getcwd()
checkpoint_dir = os.path.join(root_directory, checkpoint_no)
model_name_temp = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, model_name + '.h5')
model_reloaded.save(model_name_temp)
# Deletion of the automatically created folder under Model Checkpoint File.
folder_name_temp = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, model_name)
shutil.rmtree(folder_name_temp, ignore_errors=True)best_model = load_model(model_name_temp)4.12 Model Testing
test_loss, test_acc = best_model.evaluate(test_features, test_labels,
batch_size = n_batch_size)
print()
print('Test Accuracy:', test_acc)
In order to have all necessary metrics for a later use of the created model, we save them separately.
pk.dump(img_height, open(checkpoint_dir+ '\\' +'img_height.pkl', 'wb'))
pk.dump(img_width, open(checkpoint_dir+ '\\' +'img_width.pkl', 'wb'))
pk.dump(n_pooled_rows, open(checkpoint_dir+ '\\' +'n_pooled_rows.pkl', 'wb'))
pk.dump(n_pooled_cols, open(checkpoint_dir+ '\\' +'n_pooled_cols.pkl', 'wb'))
pk.dump(n_channels, open(checkpoint_dir+ '\\' +'n_channels.pkl', 'wb'))4.13 Test Out of the Box Pictures
# Determine Checkpoint Dir
checkpoint_dir = 'ckpt_1_CNN_with_TF_VGG19'
# Load best model
best_model = load_model(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'Cats_Dogs_CNN_TF_VGG19_epoch_30.h5')
# Load the categories
df = pd.read_csv(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'class_assignment_df_Cats_Dogs_CNN_TF_VGG19_epoch_30.csv')
df = df.sort_values(by='Allocated Number', ascending=True)
CATEGORIES = df['Category'].to_list()
# Load the used image height and width
img_height_reload = pk.load(open(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'img_height.pkl','rb'))
img_width_reload = pk.load(open(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'img_width.pkl','rb'))
# Load the used n_pooled_rows, n_pooled_cols and n_channels
n_pooled_rows_reload = pk.load(open(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'n_pooled_rows.pkl','rb'))
n_pooled_cols_reload = pk.load(open(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'n_pooled_cols.pkl','rb'))
n_channels_reload = pk.load(open(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'n_channels.pkl','rb'))
print('Model Summary :' + str(best_model.summary()))
print()
print()
print('CATEGORIES : ' + str(CATEGORIES))
print()
print('Used image height: ' + str(img_height_reload))
print('Used image width: ' + str(img_width_reload))
print()
print('Used n_pooled_rows: ' + str(n_pooled_rows))
print('Used n_pooled_cols: ' + str(n_pooled_cols))
print('Used n_channels: ' + str(n_channels))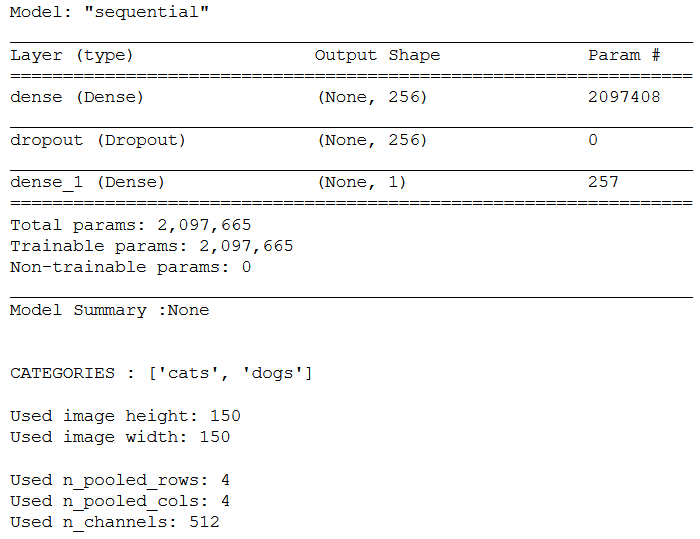
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_cat_pic_1.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = np.zeros(shape=(1, n_pooled_rows_reload, n_pooled_cols_reload, n_channels_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred, (1, n_pooled_rows_reload * n_pooled_cols_reload * n_channels_reload))
classes = (best_model.predict(img_pred) > 0.5).astype("int32")
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')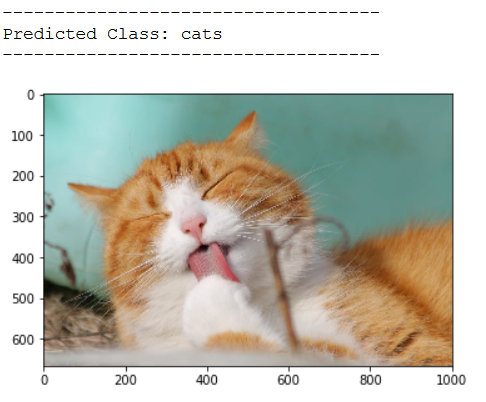
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_cat_pic_2.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = np.zeros(shape=(1, n_pooled_rows_reload, n_pooled_cols_reload, n_channels_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred, (1, n_pooled_rows_reload * n_pooled_cols_reload * n_channels_reload))
classes = (best_model.predict(img_pred) > 0.5).astype("int32")
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')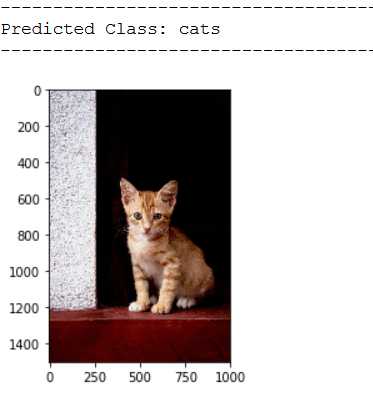
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_dog_pic_1.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = np.zeros(shape=(1, n_pooled_rows_reload, n_pooled_cols_reload, n_channels_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred, (1, n_pooled_rows_reload * n_pooled_cols_reload * n_channels_reload))
classes = (best_model.predict(img_pred) > 0.5).astype("int32")
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')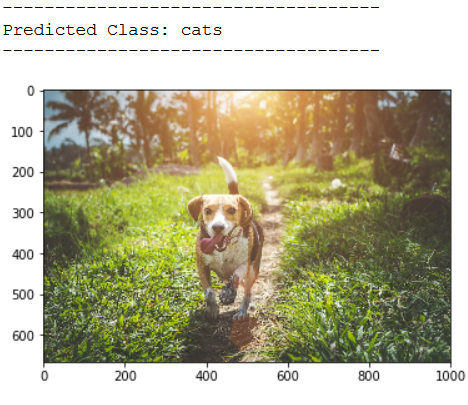
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_dog_pic_2.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = np.zeros(shape=(1, n_pooled_rows_reload, n_pooled_cols_reload, n_channels_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred, (1, n_pooled_rows_reload * n_pooled_cols_reload * n_channels_reload))
classes = (best_model.predict(img_pred) > 0.5).astype("int32")
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')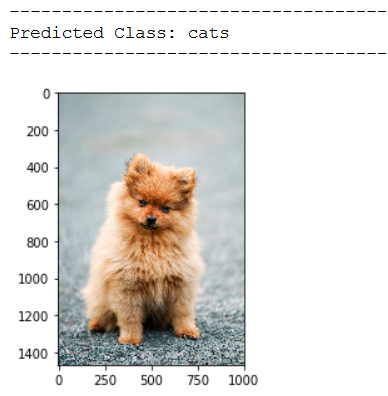
As we can see from the test images, our classifier does not yet work as desired. Let’s see if we do better with the following method.
5 Feature Extraction with Data Augmentation
For Feature Extraction without Data Augmentation, we simply used the existing trained features from VGG19 and ran them over our dataset. We then used this output as input to a standalone densely-connected classifier.
Now we will put our dense layers on top of the conv_base and run our image dataset through the entire network. Of course, this method is a lot more computationally intensive than the previous one, but it usually produces better results.
5.1 Name Definitions
checkpoint_no = 'ckpt_2_CNN_with_TF_VGG19_with_DataAug'
model_name = 'Cats_Dogs_CNN_TF_VGG19_with_DataAug_epoch_30_ES'5.2 Parameter Settings
img_height = 150
img_width = 150
input_shape = (img_height, img_width, 3)
n_batch_size = 32
n_steps_per_epoch = int(num_train_images_total / n_batch_size)
n_validation_steps = int(num_validation_images_total / n_batch_size)
n_test_steps = int(num_test_images_total / n_batch_size)
n_epochs = 30
print('Input Shape: '+'('+str(img_height)+', '+str(img_width)+', ' + str(3)+')')
print('Batch Size: ' + str(n_batch_size))
print()
print('Steps per Epoch: ' + str(n_steps_per_epoch))
print()
print('Validation Steps: ' + str(n_validation_steps))
print('Test Steps: ' + str(n_test_steps))
print()
print('Number of Epochs: ' + str(n_epochs))
5.3 Instantiating the VGG19 convolutional base
VGG19_base = VGG19(weights='imagenet',
include_top=False,
input_shape=input_shape)
conv_base = VGG19_base5.4 Instantiating a densely connected classifier
5.4.1 Layer Structure
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(conv_base)
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))model.summary()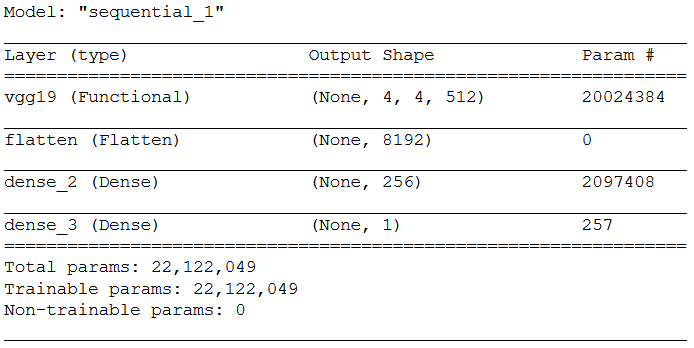
print('Number of trainable weights before freezing the conv base:', len(model.trainable_weights))
conv_base.trainable = False
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(conv_base)
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))model.summary()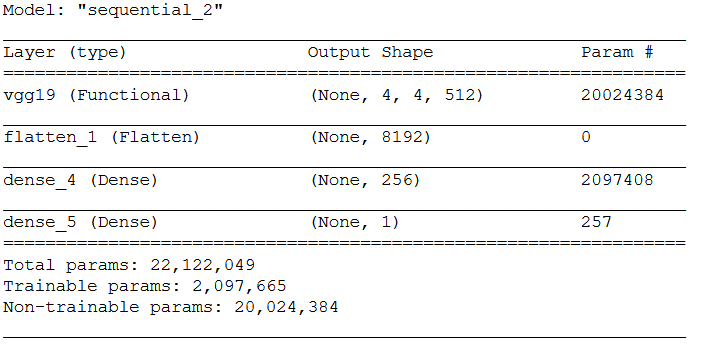
print('Number of trainable weights after freezing the conv base:', len(model.trainable_weights))
5.4.2 Configuring the model for training
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])5.4.3 Using ImageDataGenerator
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1./255,
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,)
validation_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=n_batch_size,
class_mode='binary')
validation_generator = validation_datagen.flow_from_directory(
validation_dir,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=n_batch_size,
class_mode='binary')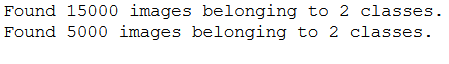
5.5 Callbacks
# Prepare a directory to store all the checkpoints.
checkpoint_dir = checkpoint_no
if not os.path.exists(checkpoint_dir):
os.makedirs(checkpoint_dir)keras_callbacks = [ModelCheckpoint(filepath = checkpoint_dir,
monitor='val_loss', save_best_only=True, mode='auto'),
EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=5, mode='auto',
min_delta = 0, verbose=1)]5.6 Fitting the model
history = model.fit(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=n_steps_per_epoch,
epochs=n_epochs,
validation_data=validation_generator,
validation_steps=n_validation_steps,
callbacks=keras_callbacks)
5.7 Obtaining the best model values
hist_df = pd.DataFrame(history.history)
hist_df['epoch'] = hist_df.index + 1
cols = list(hist_df.columns)
cols = [cols[-1]] + cols[:-1]
hist_df = hist_df[cols]
hist_df.to_csv(checkpoint_no + '/' + 'history_df_' + model_name + '.csv')
hist_df.head()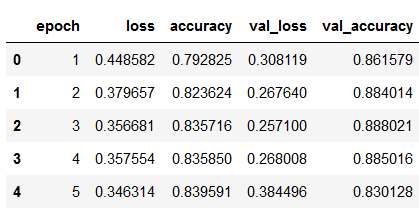
values_of_best_model = hist_df[hist_df.val_loss == hist_df.val_loss.min()]
values_of_best_model
5.8 Obtaining class assignments
class_assignment = train_generator.class_indices
df = pd.DataFrame([class_assignment], columns=class_assignment.keys())
df_stacked = df.stack()
df_temp = pd.DataFrame(df_stacked).reset_index().drop(['level_0'], axis=1)
df_temp.columns = ['Category', 'Allocated Number']
df_temp.to_csv(checkpoint_no + '/' + 'class_assignment_df_' + model_name + '.csv')
print('Class assignment:', str(class_assignment))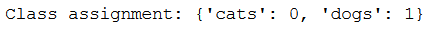
5.9 Validation
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()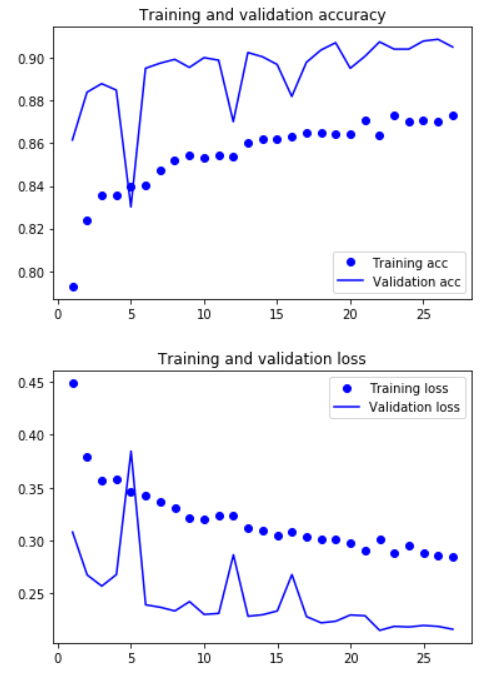
5.10 Load best model
# Loading the automatically saved model
model_reloaded = load_model(checkpoint_no)
# Saving the best model in the correct path and format
root_directory = os.getcwd()
checkpoint_dir = os.path.join(root_directory, checkpoint_no)
model_name_temp = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, model_name + '.h5')
model_reloaded.save(model_name_temp)
# Deletion of the automatically created folders/.pb file under Model Checkpoint File.
folder_name_temp1 = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, 'assets')
folder_name_temp2 = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, 'variables')
file_name_temp = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, 'saved_model.pb')
shutil.move(file_name_temp, folder_name_temp1)
shutil.rmtree(folder_name_temp1, ignore_errors=True)
shutil.rmtree(folder_name_temp2, ignore_errors=True)best_model = load_model(model_name_temp)5.11 Model Testing
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
test_dir,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=n_batch_size,
class_mode='binary')
test_loss, test_acc = best_model.evaluate(test_generator, steps=n_test_steps)
print()
print('Test Accuracy:', test_acc)
Once again, we save all the necessary metrics.
pk.dump(img_height, open(checkpoint_dir+ '\\' +'img_height.pkl', 'wb'))
pk.dump(img_width, open(checkpoint_dir+ '\\' +'img_width.pkl', 'wb'))Our final folder structure now looks like this:
5.12 Test Out of the Box Pictures
# Determine Checkpoint Dir
checkpoint_dir = 'ckpt_2_CNN_with_TF_VGG19_with_DataAug'
# Load best model
best_model = load_model(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'Cats_Dogs_CNN_TF_VGG19_with_DataAug_epoch_30_ES.h5')
# Load the categories
df = pd.read_csv(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'class_assignment_df_Cats_Dogs_CNN_TF_VGG19_with_DataAug_epoch_30_ES.csv')
df = df.sort_values(by='Allocated Number', ascending=True)
CATEGORIES = df['Category'].to_list()
# Load the used image height and width
img_height_reload = pk.load(open(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'img_height.pkl','rb'))
img_width_reload = pk.load(open(checkpoint_dir + '/' + 'img_width.pkl','rb'))
print('Model Summary :' + str(best_model.summary()))
print()
print()
print('CATEGORIES : ' + str(CATEGORIES))
print()
print('Used image height: ' + str(img_height_reload))
print('Used image width: ' + str(img_width_reload))
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_cat_pic_1.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = (best_model.predict(img_pred) > 0.5).astype("int32")
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_cat_pic_2.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = (best_model.predict(img_pred) > 0.5).astype("int32")
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')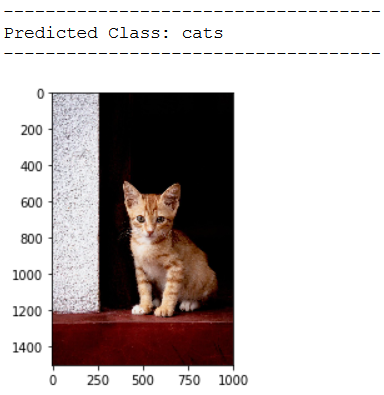
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_dog_pic_1.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = (best_model.predict(img_pred) > 0.5).astype("int32")
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_dog_pic_2.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = (best_model.predict(img_pred) > 0.5).astype("int32")
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')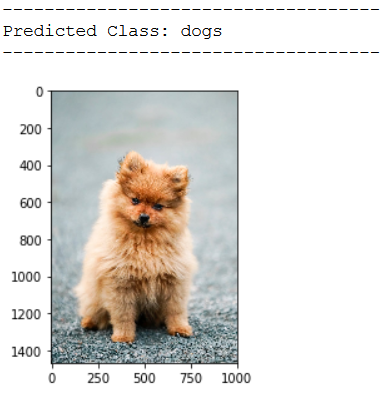
This is exactly how our image classifier is supposed to work.
6 Conclusion
In this post I showed how you can use pre-trained networks to improve the performance of your classifier.
7 Link to the GitHub Repository
Here is the link to my GitHub repository where I have listed all necessary steps: Computer Vision: CNN with Transfer Learning for binary Classification
References
The content of the entire post was created using the following sources:
Chollet, F. (2018). Deep learning with Python (Vol. 361). New York: Manning.