- 1 Introduction
- 2 Import the libraries
- 3 Data pre-processing
- 4 CNN with Data Augmentation
- 5 Test Out of the Box Pictures
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 Link to the GitHub Repository
1 Introduction
In my last post, we saw how Convolutional Neural Networks can be used to make binary classifications of image data. Of course you also have the possibility to do multi-class classifications. This is what I will introduce in this post.
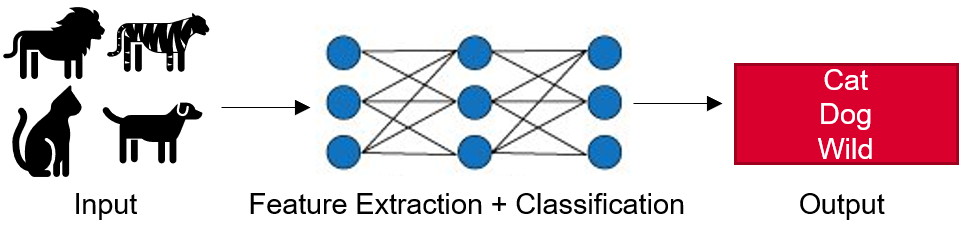
Most of the steps are the same as for binary classification. If new ones are added, I will of course explain them in this post.
For this publication I used the images from the Animal Faces dataset from the statistics platform “Kaggle”. You can download the used data from my “GitHub Repository”.
2 Import the libraries
from preprocessing_multi_CNN import Train_Validation_Test_Split
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import pickle as pk
import os
import shutil
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from keras import layers
from keras import models
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.models import load_model3 Data pre-processing
3.1 Train-Validation-Test Split
This step is already known from the Convolutional Neural Network post. Read there again if you have questions about it.
Again, I have written the necessary preparation steps as described in the Automate The Boring Stuff post into a separate .py file.
I have chosen the percentage distribution as follows:
- Trainings Part: 60%
- Validation Part: 20%
- Testing Part: 20%
You can also download the .py file mentioned before from my “GitHub Repository”.
Place this file (preprocessing_multi_CNN.py) next to the folders cats, dogs and wilds and start your Jupyter notebook from here.
c_train, d_train, w_train, \
c_val, d_val, w_val, \
c_test, d_test, w_test = Train_Validation_Test_Split('cats', 'dogs', 'wilds')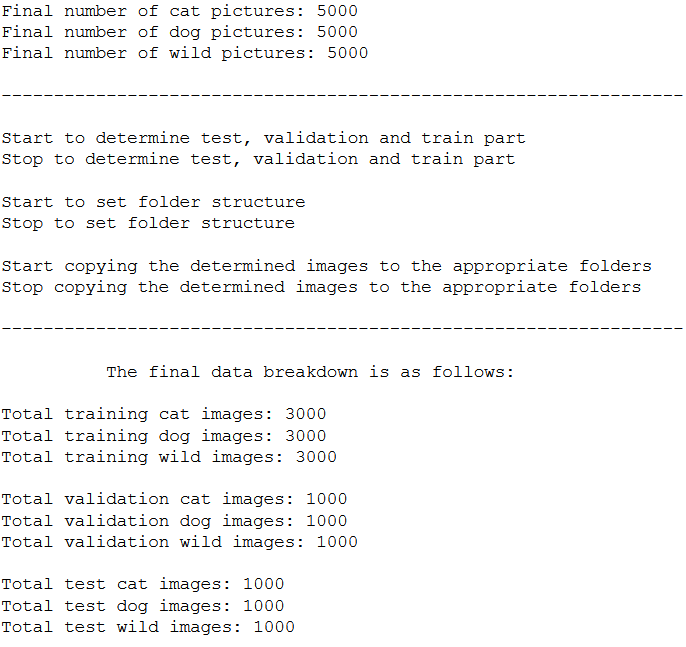
As you can read in the function itself it returns 9 values:
- list_cats_training (int): List of randomly selected images for the training part of the first category
- list_dogs_training (int): List of randomly selected images for the training part of the second category
- list_wilds_training (int): List of randomly selected images for the training part of the third category
- list_cats_validation (int): List of randomly selected images for the validation part of the first category
- list_dogs_validation (int): List of randomly selected images for the validation part of the second category
- list_wilds_validation (int): List of randomly selected images for the validation part of the third category
- list_cats_test (int): List of randomly selected images for the test part of the first category
- list_dogs_test (int): List of randomly selected images for the test part of the second category
- list_wilds_test (int): List of randomly selected images for the test part of the third category
3.2 Obtaining the lists of randomly selected images
To make the naming of the output of the function more meaningful I rename it accordingly:
list_cats_training = c_train
list_dogs_training = d_train
list_wilds_training = w_train
list_cats_validation = c_val
list_dogs_validation = d_val
list_wilds_validation = w_val
list_cats_test = c_test
list_dogs_test = d_test
list_wilds_test = w_test3.3 Determination of the directories
Here I specify the path where the neural network can later find the data.
root_directory = os.getcwd()
train_dir = os.path.join(root_directory, 'animals\\train')
validation_dir = os.path.join(root_directory, 'animals\\validation')
test_dir = os.path.join(root_directory, 'animals\\test')3.4 Obtain the total number of training, validation and test images
Here I’m not interested in reissuing the folder sizes but much more in getting the total number of images for the respective areas.
num_cats_img_train = len(list_cats_training)
num_dogs_img_train = len(list_dogs_training)
num_wilds_img_train = len(list_wilds_training)
num_train_images_total = num_cats_img_train + num_dogs_img_train + num_wilds_img_train
print('Total training cat images: ' + str(num_cats_img_train))
print('Total training dog images: ' + str(num_dogs_img_train))
print('Total training wild images: ' + str(num_wilds_img_train))
print()
print('Total training images: ' + str(num_train_images_total))
num_cats_img_validation = len(list_cats_validation)
num_dogs_img_validation = len(list_dogs_validation)
num_wilds_img_validation = len(list_wilds_validation)
num_validation_images_total = num_cats_img_validation + num_dogs_img_validation + num_wilds_img_validation
print('Total validation cat images: ' + str(num_cats_img_validation))
print('Total validation dog images: ' + str(num_dogs_img_validation))
print('Total validation wild images: ' + str(num_wilds_img_validation))
print()
print('Total validation images: ' + str(num_validation_images_total))
num_cats_img_test = len(list_cats_test)
num_dogs_img_test = len(list_dogs_test)
num_wilds_img_test = len(list_wilds_test)
num_test_images_total = num_cats_img_test + num_dogs_img_test + num_wilds_img_test
print('Total test cat images: ' + str(num_cats_img_test))
print('Total test dog images: ' + str(num_dogs_img_test))
print('Total test wild images: ' + str(num_wilds_img_test))
print()
print('Total test images: ' + str(num_test_images_total))
4 CNN with Data Augmentation
4.1 Name Definitions
I always want to save the created models right away. For this purpose, I specify the name of the folder in which the future model is to be saved and the name that the model itself is to receive.
checkpoint_no = 'ckpt_1_CNN_with_augm'
model_name = 'Animals_CNN_4_Conv_F32_64_128_128_epoch_60_es'4.2 Parameter Settings
I have already described the parameters and their meaning in detail. Otherwise you can also read here again.
img_height = 150
img_width = 150
input_shape = (img_height, img_width, 3)
n_batch_size = 32
n_steps_per_epoch = int(num_train_images_total / n_batch_size)
n_validation_steps = int(num_validation_images_total / n_batch_size)
n_test_steps = int(num_test_images_total / n_batch_size)
n_epochs = 60
num_classes = len(os.listdir(train_dir))
print('Input Shape: '+'('+str(img_height)+', '+str(img_width)+', ' + str(3)+')')
print('Batch Size: ' + str(n_batch_size))
print()
print('Steps per Epoch: ' + str(n_steps_per_epoch))
print()
print('Validation Steps: ' + str(n_validation_steps))
print('Test Steps: ' + str(n_test_steps))
print()
print('Number of Epochs: ' + str(n_epochs))
print()
print('Number of Classes: ' + str(num_classes))
4.3 Instantiating a CNN with Data Augmentation
4.3.1 Layer Structure
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu',input_shape=input_shape))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dropout(0.5))
model.add(layers.Dense(512, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))This time I am not using the sigmoid function but the softmax, because this is a multi-class classification problem. Also the last dense layer is not set to 1, as it was the case with the binary classification, but now gets the number of possible classes to be learned during model training (here 3).
model.summary()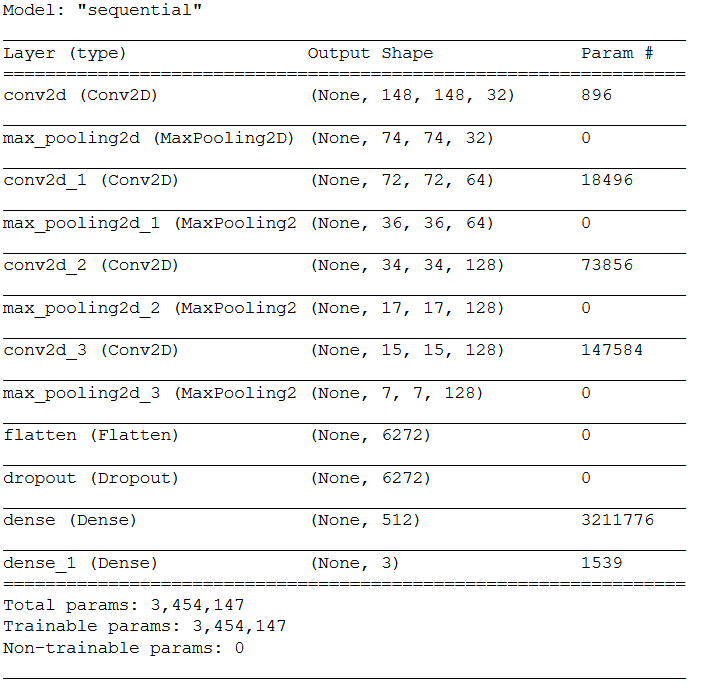
4.3.2 Configuring the model for training
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])4.3.3 Using ImageDataGenerator with data augmentation
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1./255,
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,)
validation_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=n_batch_size,
class_mode='categorical')
validation_generator = validation_datagen.flow_from_directory(
validation_dir,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=n_batch_size,
class_mode='categorical')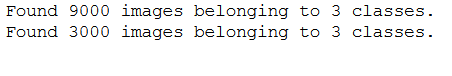
4.4 Callbacks
# Prepare a directory to store all the checkpoints.
checkpoint_dir = './'+ checkpoint_no
if not os.path.exists(checkpoint_dir):
os.makedirs(checkpoint_dir)keras_callbacks = [ModelCheckpoint(filepath = checkpoint_dir + '/' + model_name,
monitor='val_loss', save_best_only=True, mode='auto'),
EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=7, mode='auto',
min_delta = 0, verbose=1)]4.5 Fitting the model
history = model.fit(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=n_steps_per_epoch,
epochs=n_epochs,
validation_data=validation_generator,
validation_steps=n_validation_steps,
callbacks=keras_callbacks) …
…
4.6 Obtaining the best model values
hist_df = pd.DataFrame(history.history)
hist_df['epoch'] = hist_df.index + 1
cols = list(hist_df.columns)
cols = [cols[-1]] + cols[:-1]
hist_df = hist_df[cols]
hist_df.to_csv(checkpoint_no + '/' + 'history_df_' + model_name + '.csv')
hist_df.head()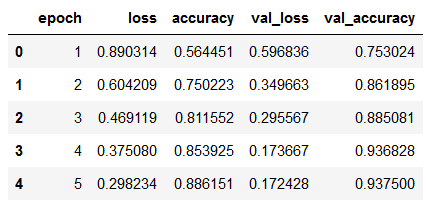
values_of_best_model = hist_df[hist_df.val_loss == hist_df.val_loss.min()]
values_of_best_model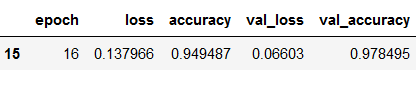
4.7 Obtaining class assignments
class_assignment = train_generator.class_indices
df = pd.DataFrame([class_assignment], columns=class_assignment.keys())
df_stacked = df.stack()
df_temp = pd.DataFrame(df_stacked).reset_index().drop(['level_0'], axis=1)
df_temp.columns = ['Category', 'Allocated Number']
df_temp.to_csv(checkpoint_no + '/' + 'class_assignment_df_' + model_name + '.csv')
print('Class assignment:', str(class_assignment))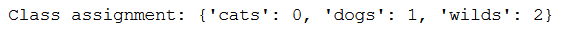
4.8 Validation
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()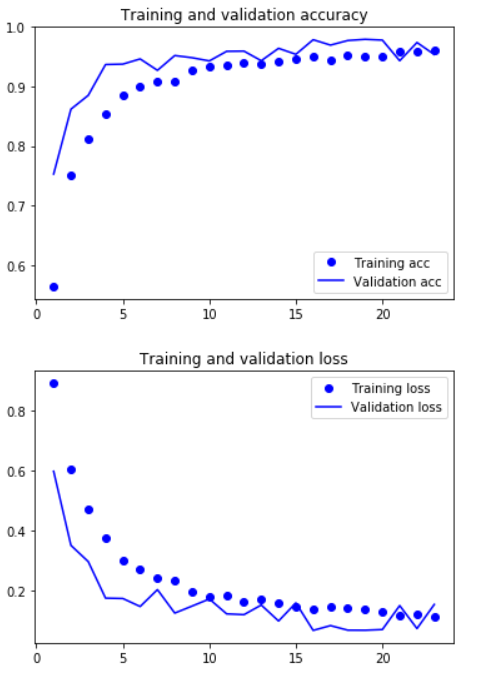
4.9 Load best model
# Loading the automatically saved model
model_reloaded = load_model(checkpoint_no + '/' + model_name)
# Saving the best model in the correct path and format
root_directory = os.getcwd()
checkpoint_dir = os.path.join(root_directory, checkpoint_no)
model_name_temp = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, model_name + '.h5')
model_reloaded.save(model_name_temp)
# Deletion of the automatically created folder under Model Checkpoint File.
folder_name_temp = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, model_name)
shutil.rmtree(folder_name_temp, ignore_errors=True)best_model = load_model(model_name_temp)4.10 Model Testing
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
test_dir,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=n_batch_size,
class_mode='categorical')
test_loss, test_acc = best_model.evaluate(test_generator, steps=n_test_steps)
print()
print('Test Accuracy:', test_acc)
Not bad.
pk.dump(img_height, open(checkpoint_dir+ '\\' +'img_height.pkl', 'wb'))
pk.dump(img_width, open(checkpoint_dir+ '\\' +'img_width.pkl', 'wb'))The final folder structure should now look like this:

5 Test Out of the Box Pictures
Again, for this model training, I have saved images that have not yet appeared in the entire data set. With them I now want to check how well my model can generalize. To do this, we load the categories and some of the training metrics used.
# Load the categories
df = pd.read_csv('ckpt_1_CNN_with_augm/class_assignment_df_Animals_CNN_4_Conv_F32_64_128_128_epoch_60_es.csv')
df = df.sort_values(by='Allocated Number', ascending=True)
CATEGORIES = df['Category'].to_list()
# Load the used image height and width
img_height_reload = pk.load(open("ckpt_1_CNN_with_augm/img_height.pkl",'rb'))
img_width_reload = pk.load(open("ckpt_1_CNN_with_augm/img_width.pkl",'rb'))
print('CATEGORIES : ' + str(CATEGORIES))
print()
print('Used image height: ' + str(img_height_reload))
print('Used image width: ' + str(img_width_reload))
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_cat_pic_1.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = np.argmax(best_model.predict(img_pred), axis=-1)
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')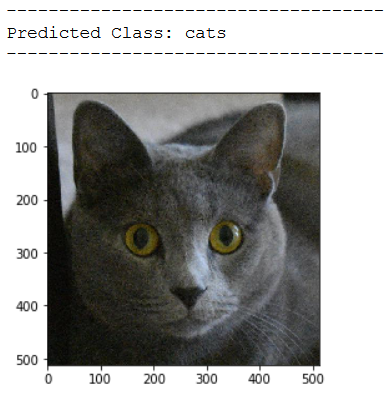
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_cat_pic_2.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = np.argmax(best_model.predict(img_pred), axis=-1)
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_cat_pic_3.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = np.argmax(best_model.predict(img_pred), axis=-1)
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')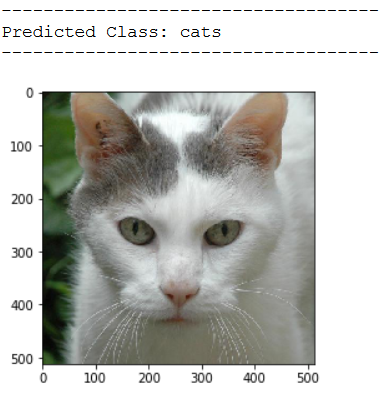
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_dog_pic_1.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = np.argmax(best_model.predict(img_pred), axis=-1)
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_dog_pic_2.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = np.argmax(best_model.predict(img_pred), axis=-1)
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')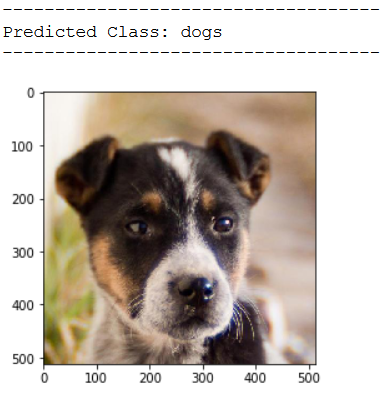
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_dog_pic_3.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = np.argmax(best_model.predict(img_pred), axis=-1)
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_wild_pic_1.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = np.argmax(best_model.predict(img_pred), axis=-1)
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_wild_pic_2.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = np.argmax(best_model.predict(img_pred), axis=-1)
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')
img_pred = cv2.imread('out of the box pic/test_wild_pic_3.jpg')
print(plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_pred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
img_pred = cv2.resize(img_pred,(img_height_reload,img_width_reload))
img_pred = np.reshape(img_pred,[1,img_height_reload,img_width_reload,3])
classes = np.argmax(best_model.predict(img_pred), axis=-1)
print()
print('------------------------------------')
print('Predicted Class: ' + CATEGORIES[int(classes[0])])
print('------------------------------------')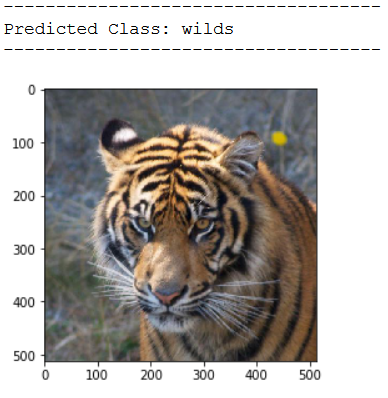
6 Conclusion
In addition to my post CNNs for binary Classification, I have shown here how to make multi-class classifications using Convolutional Neural Networks.
7 Link to the GitHub Repository
Here is the link to my GitHub repository where I have listed all necessary steps: Computer Vision: CNN for Multi-Class Classification
References
The content of the entire post was created using the following sources:
Chollet, F. (2018). Deep learning with Python (Vol. 361). New York: Manning.