1 Introduction
Now we come to another sub-area regarding text pre-processing: The removal of individual characters.
For this publication the processed dataset Amazon Unlocked Mobile from the statistic platform “Kaggle” was used as well as the created Example String. You can download both files from my “GitHub Repository”.
2 Import the Libraries and the Data
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import pickle as pk
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import unicodedata
import re
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.corpus import wordnet
from nltk import pos_tag
from nltk import ne_chunk
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
from nltk.stem.wordnet import WordNetLemmatizer
from nltk.probability import FreqDist
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from wordcloud import WordCloudpd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', 30)df = pd.read_csv('Amazon_Unlocked_Mobile_small_Part_III.csv')
df.head(3).T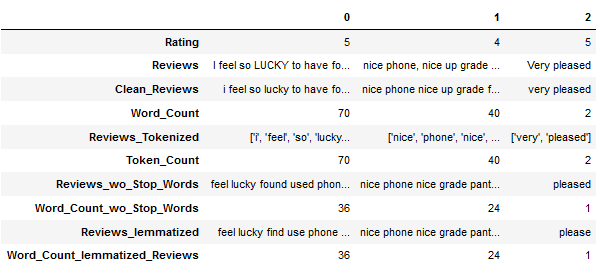
df['Reviews_lemmatized'] = df['Reviews_lemmatized'].astype(str)clean_text_lemmatized_v_a = pk.load(open("clean_text_lemmatized_v_a.pkl",'rb'))
clean_text_lemmatized_v_a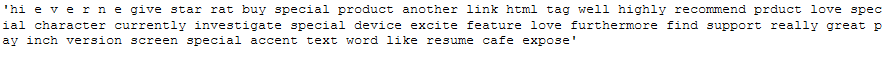
3 Definition of required Functions
All functions are summarized here. I will show them again where they are used during this post if they are new and have not been explained yet.
def word_count_func(text):
'''
Counts words within a string
Args:
text (str): String to which the function is to be applied, string
Returns:
Number of words within a string, integer
'''
return len(text.split())def remove_single_char_func(text, threshold=1):
'''
Removes single characters from string, if present
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Removes words whose length falls below the threshold (by default = 1)
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
Returns:
String with removed words whose length was below the threshold (by default = 1)
'''
threshold = threshold
words = word_tokenize(text)
text = ' '.join([word for word in words if len(word) > threshold])
return text4 Text Pre-Processing
4.1 (Text Cleaning)
I have already described this part in an earlier post. See here: Text Cleaning
4.2 (Tokenization)
I have already described this part in an earlier post. See here: Text Pre-Processing II-Tokenization
4.3 (Stop Words)
I have already described this part in an earlier post. See here: Text Pre-Processing II-Stop Words
4.4 (Digression: POS & NER)
I have already described this part in the previous post. See here: Text Pre-Processing III-POS & NER
4.5 (Normalization)
I have already described this part in the previous post. See here: Text Pre-Processing III-Normalization
4.6 Removing Single Characters
In some cases (as is the case with the Example String), single characters may still be present in a string (after using Stop Word Removal etc.).
Let’s look at the following example sentence where I am aware that some characters would no longer be there after our previous steps. This example is just to show how the function works.
text_for_remove_single_char = \
"This is an example string with numbers like 5 or 10 and single characters like a, b and c."
text_for_remove_single_char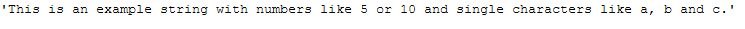
def remove_single_char_func(text, threshold=1):
'''
Removes single characters from string, if present
Step 1: Use word_tokenize() to get tokens from string
Step 2: Removes words whose length falls below the threshold (by default = 1)
Args:
text (str): String to which the functions are to be applied, string
Returns:
String with removed words whose length was below the threshold (by default = 1)
'''
threshold = threshold
words = word_tokenize(text)
text = ' '.join([word for word in words if len(word) > threshold])
return textNow we apply the function to our example sentence (text_for_remove_single_char) with the default settings (threshold=1).
remove_single_char_func(text_for_remove_single_char)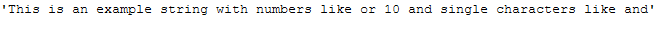
Depending on the case, the threshold can also be set high (for example, to 2 characters).
remove_single_char_func(text_for_remove_single_char, threshold=2)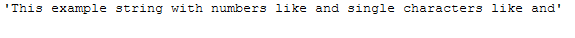
4.6.1 Application to the Example String
I will continue at this point with the edited example string ‘clean_text_lemmatized_v_a’ from the last blog, which we already loaded at the beginning of this post.
clean_text_lemmatized_v_a
clean_text_wo_single_char = remove_single_char_func(clean_text_lemmatized_v_a)
clean_text_wo_single_char
4.6.2 Application to the DataFrame
df.head(3).T
4.6.2.1 With Character Length = 1 (default settings)
df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char'] = df['Reviews_lemmatized'].apply(remove_single_char_func)
df['Word_Count_cleaned_Reviews_wo_single_char'] = df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char'].apply(word_count_func)
df.head(3).T
print('Average of lemmatized words counted: ' + str(df['Word_Count_lemmatized_Reviews'].mean()))
print('Average of cleaned words wo single char counted: ' + str(df['Word_Count_cleaned_Reviews_wo_single_char'].mean()))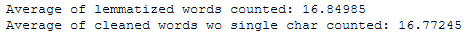
Again, we see that some words have been removed. Let’s have a look and see what they are.
df_subset = df[['Reviews_lemmatized', 'Word_Count_lemmatized_Reviews',
'Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char', 'Word_Count_cleaned_Reviews_wo_single_char']]
df_subset['Diff'] = df_subset['Word_Count_lemmatized_Reviews'] - \
df_subset['Word_Count_cleaned_Reviews_wo_single_char']
df_subset = df_subset[(df_subset["Diff"] != 0)]
df_subset = df_subset.sort_values(by='Diff', ascending=False)
df_subset.head().T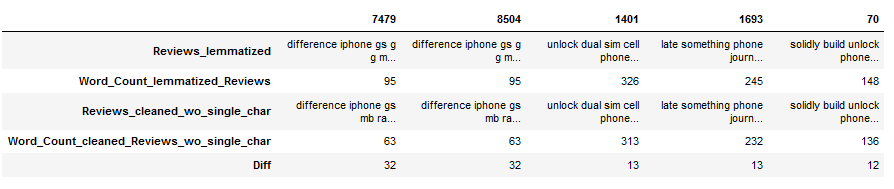
df_subset['Reviews_lemmatized'].iloc[0]
df_subset['Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char'].iloc[0]
# Original text:
df[(df.index == 7479)]['Reviews'].iloc[0]
Conclusion: By removing single characters you do not necessarily run the risk of losing valuable information from the text. Now, of course, the question arises whether you need information like millimeters (mm) or whether you also remove them with the remove_single_char function if you set the threshold to 2.
Let’s try it out.
4.6.2.2 With Character Length = 2
Now let’s try it with a higher threshold (here 2) and see if valuable information would be lost or not.
df["Reviews_cleaned_wo_char_length_2"] = df.apply(lambda x: remove_single_char_func(x["Reviews_lemmatized"],
threshold=2), axis = 1)
df['Word_Count_cleaned_Reviews_wo_char_length_2'] = df['Reviews_cleaned_wo_char_length_2'].apply(word_count_func)
df.head(3).T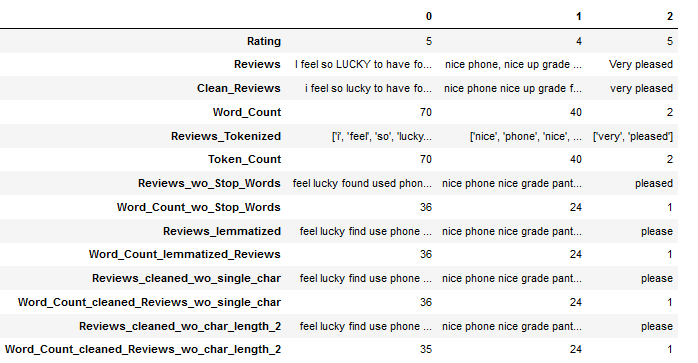
print('Average of lemmatized words counted: ' + str(df['Word_Count_lemmatized_Reviews'].mean()))
print('Average of cleaned words wo single char counted: ' + str(df['Word_Count_cleaned_Reviews_wo_single_char'].mean()))
print('Average of cleaned words wo char length 2 counted: ' + str(df['Word_Count_cleaned_Reviews_wo_char_length_2'].mean()))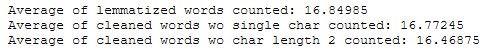
df_subset = df[['Reviews_lemmatized', 'Word_Count_lemmatized_Reviews',
'Reviews_cleaned_wo_char_length_2', 'Word_Count_cleaned_Reviews_wo_char_length_2']]
df_subset['Diff'] = df_subset['Word_Count_lemmatized_Reviews'] - \
df_subset['Word_Count_cleaned_Reviews_wo_char_length_2']
df_subset = df_subset[(df_subset["Diff"] != 0)]
#df_subset = df_subset.sort_values(by='Diff', ascending=False)
df_subset.head().T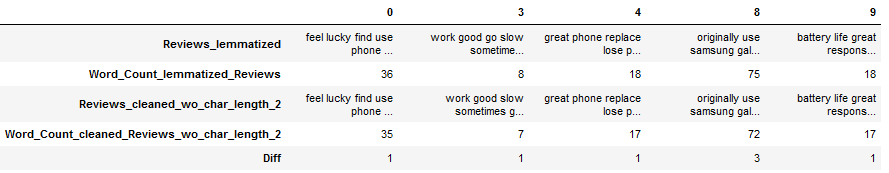
df_subset['Reviews_lemmatized'].iloc[1]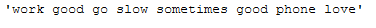
df_subset['Reviews_cleaned_wo_char_length_2'].iloc[1]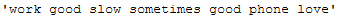
# Original text:
df[(df.index == 3)]['Reviews'].iloc[0]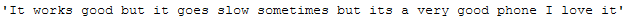
Conclusion: The average number of words could be reduced again with a threshold of 2, which would definitely help our later model training in terms of complexity and training speed. However, words like ‘go’ that might be profitable are also deleted. A possibility here would be to use another lemmatizer (for example the one in the norm_lemm_POS_tag function), where the verbs are not converted into their base form. So ‘went’ or ‘gone’ would not become ‘go’, which in turn would not be removed by the remove_single_char function with a threshold of 2.
In the following I will continue to work with the column ‘Reviews_cleaned_wo_single_char’, where we only removed single characters with a length of 1.
5 Conclusion
In this post, I showed how to remove single characters from texts and spot check the generated results.
I save the edited DataFrame and Example String again for subsequent use.
pk.dump(clean_text_wo_single_char, open('clean_text_wo_single_char.pkl', 'wb'))
df.to_csv('Amazon_Unlocked_Mobile_small_Part_IV.csv', index = False)Next, I will continue with the topic of text exploration.