1 Introduction
NumPy is a library of Python that makes it easy to handle vectors, matrices, or large multidimensional arrays in general. In addition to the data structures, NumPy also offers efficiently implemented functions for numerical calculations.
Loading the libraries
import numpy as np2 Attributes of NumPy Arrays
np.random.seed(0)
x1 = np.random.randint(10, size = 6)
#One-dimensional array
x2 = np.random.randint(10, size = (3, 4))
#Two-dimensional array
x3 = np.random.randint(10, size = (3, 4, 5))
#Three-dimensional arrayprint("x3 ndim: ", x3.ndim)
print("x3 shape: ", x3.shape)
print("x3 size: ", x3.size)
3 Indexing of Arrays
3.1 Access to individual elements
x1
print(x1[0])
print(x1[1])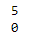
print(x1[-1])
print(x1[-2])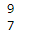
x2
x2[0, 0]
3.2 via Slicing
x1[:3] #first 3 elements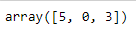
x1[3:] #from element 3 onwards
x1[::2] #select every second element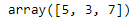
x1[::-1] #all elements in reverse order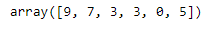
3.3 Multidimensional subsets of an Array
x2
x2[:2, :3] #two rows, three columns
4 Reshape
RESHAPE = np.arange(1, 10)
RESHAPE
RESHAPE.reshape((3, 3))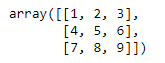
5 Concatenate Arrays
x = np.array([1,2,3])
y = np.array([3,2,1])
np.concatenate([x, y])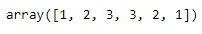
z = [88, 99, 100]
show_con = np.concatenate([x, y, z])
show_con
6 Split Arrays
x1, x2, x3 = np.split(show_con, [3, 6])
print(x1, x2, x3)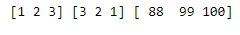
7 UFuncs
7.1 Array-Arithmetik
x = np.array([1,2,3])
print("x - 3 =", x - 3)
print("x + 3 =", x + 3)
print("x * 2 =", x * 2)
print("x / 2 =", x / 2)
print("x ** 2 =", x ** 2)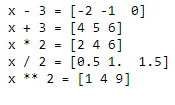
7.2 Exponential function
x = np.array([1,2,3])
print("e^x =", np.exp(x))
print("2^x =", np.exp2(x))
print("3^x =", np.power(3, x))
7.3 Logarithm
x = np.array([1, 2, 4, 10])
print("x =", x)
print("ln(x) =", np.log(x))
print("log2(x) =", np.log2(x))
print("log10(x) =", np.log10(x))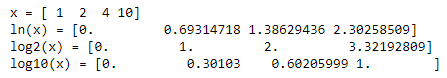
7.4 Comparison operators
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
x < 3 # less than
x >= 3 # greater or equal
x != 3 # unequal
x == 3 # equal
print("x < 3", x < 3)
print("x >= 3", x >= 3)
print("x != 3", x != 3)
print("x == 3", x == 3)
np.count_nonzero(x < 6)
#how many values are less than 6 ? 
np.any(x < 8)
#are there varlues over 8 ?
np.all(x < 10)
#are all values less than 10 ? 
8 Aggregation
MyBigArray = np.random.random(1000000)print("sum =", np.sum(MyBigArray))
print("min =", np.min(MyBigArray))
print("max =", np.max(MyBigArray))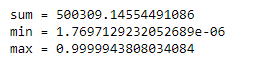
8.1 Multi-dimensional aggregation
MultiArray = np.random.random((3, 4))
print(MultiArray)
MultiArray.sum()
#sum of whole array
MultiArray.min(axis=0)
#min of a column
MultiArray.max(axis=1)
#max of a row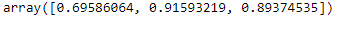
9 Timing of functions
test = np.random.random(1000000)
%timeit sum(test)
%timeit np.sum(test)
10 Conclusion
NumPy is a very useful library from Python. In my opinion, their use is essential in data science.