1 Introduction
There are several ways to generate new variables in Python. Below the most common methods will be shown.
For this post the dataset flight from the statistic platform “Kaggle” was used. You can download it from my GitHub Repository.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as npflight = pd.read_csv("path/to/file/flight.csv")2 Normal Calculation
We’ll start with the two columns Scheduled_Departure and Departure_Time from the dataset flight.
flight2 = flight.copy().filter(['Scheduled_Departure', 'Departure_Time'])
flight2.head()
flight2['new_Delay'] = flight2.Scheduled_Departure - flight2.Departure_Time
flight2.head()
3 If-else statements
flight2['new_Delay_txt'] = np.where(flight2['new_Delay']>=0, 'no delay', 'delayed')
flight2.head()
4 Multiple If-else statements
4.1 with conditional output values
def new_Delay_detailed(df):
if (df['new_Delay'] >= 45):
return 'over time'
elif (df['new_Delay'] < 45) and (df['new_Delay'] > 0):
return 'in time'
elif (df['new_Delay'] <= 0):
return 'delayed'
flight2['new_Delay_detailed'] = flight2.apply(new_Delay_detailed, axis = 1)
flight2.head()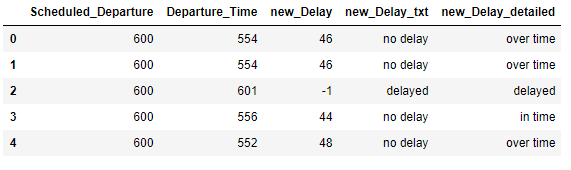
The function can also be written even more simply like this:
def new_Delay_detailed2(new_Delay):
if new_Delay >= 45:
return 'over time'
if new_Delay < 45 and new_Delay > 0:
return 'in time'
if new_Delay <= 0:
return 'delayed'
flight2['new_Delay_detailed2'] = flight2['new_Delay'].apply(new_Delay_detailed2)or even simpler:
def new_Delay_detailed3(new_Delay):
if new_Delay >= 45:
return 'over time'
if new_Delay <= 0:
return 'delayed'
else:
return 'in time'
flight2['new_Delay_detailed3'] = flight2['new_Delay'].apply(new_Delay_detailed3)I did not execute the last two commands in this notebook, otherwise it would become too confusing.
4.2 with conditional calculation
Of course there are also situations in which we do not only need a certain playback depending on the condition. The following example shows how a calculated value is output (depending on the condition).
Imagine that we have transaction data with different currencies available:
df = pd.DataFrame({'Transaction': ['46568454684', '89844548864', '90487651685'],
'Amount': [22,100,13],
'Currancy': ['EUR', 'CHF', 'EUR']})
df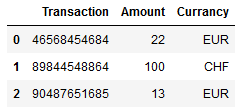
Now we want to convert the CHF to EUR with a certain exchange rate so that we have a column with the same currency (here EUR).
exchange_rate_CHF_EUR = 0.94EUR = df['Amount']
CHF_in_EUR = df['Amount']*exchange_rate_CHF_EUR
df['Amount_converted_into_EUR'] = np.where(df['Currancy']== 'EUR', EUR, CHF_in_EUR)
df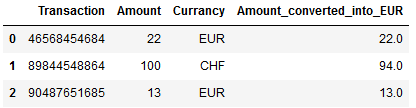
Voilà.
Now we go one step further to a similar data set, which not only contains two different currencies, but several.
df = pd.DataFrame({'Transaction': ['46568454684', '89844548864', '90487651685'],
'Amount': [22,100,100],
'Currancy': ['EUR', 'CHF', 'THB']})
df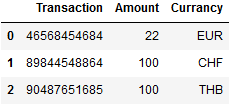
exchange_rate_CHF_EUR = 0.94
exchange_rate_THB_EUR = 0.5def converter(df):
if (df['Currancy'] == 'EUR'):
return df['Amount']
elif (df['Currancy'] == 'CHF'):
return df['Amount']*exchange_rate_CHF_EUR
elif (df['Currancy'] == 'THB'):
return df['Amount']*exchange_rate_THB_EURdf['Amount_converted_into_EUR'] = df.apply(converter, axis = 1)
df.head()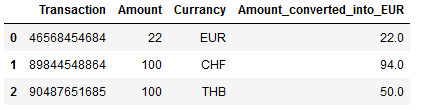
This also works with this method.
5 Row Sum
Complete row:
flight2['RowSum_complete'] = flight2.sum(axis=1)
flight2.head()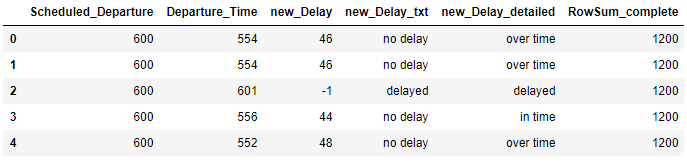
Selected columns:
flight2['RowSum_selected'] = flight2.filter(['Departure_Time', 'new_Delay']).sum(axis=1)
flight2.head()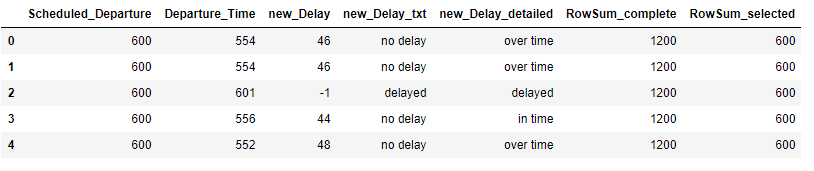
6 With a defined list
df = pd.DataFrame({"Person":
["John", "Myla", "Lewis", "John", "Myla"]})
df
The length of the list must correspond to the number of observations of the data record.
Age = ([24, np.nan, 21., 33, 26])df['Alter'] = Age
df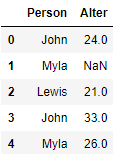
7 Conclusion
As you can see it’s quite easy to generate new columns. This can be done using simple arithmetic or self-defined if-else statements.